QWEN CHAT GITHUB HUGGING FACE MODELSCOPE DISCORD
Introduction
At the end of January this year, we launched the Qwen2.5-VL series of models, which received widespread attention and positive feedback from the community. Building on the Qwen2.5-VL series, we continued to optimize the model using reinforcement learning and open-sourced the new VL model with the beloved 32B parameter scale under the Apache 2.0 license — Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Instruct. Compared to the previously released Qwen2.5-VL series models, the features of this 32B VL model are as follows:
- Responses More Aligned with Human Preferences: Adjusted the output style to provide more detailed, better-formatted answers that align more closely with human preferences.
- Mathematical Reasoning: Significant improvement in the accuracy of solving complex mathematical problems.
- Fine-grained Image Understanding and Reasoning: Enhanced accuracy and detailed analysis in tasks such as image parsing, content recognition, and visual logic deduction.
Performance
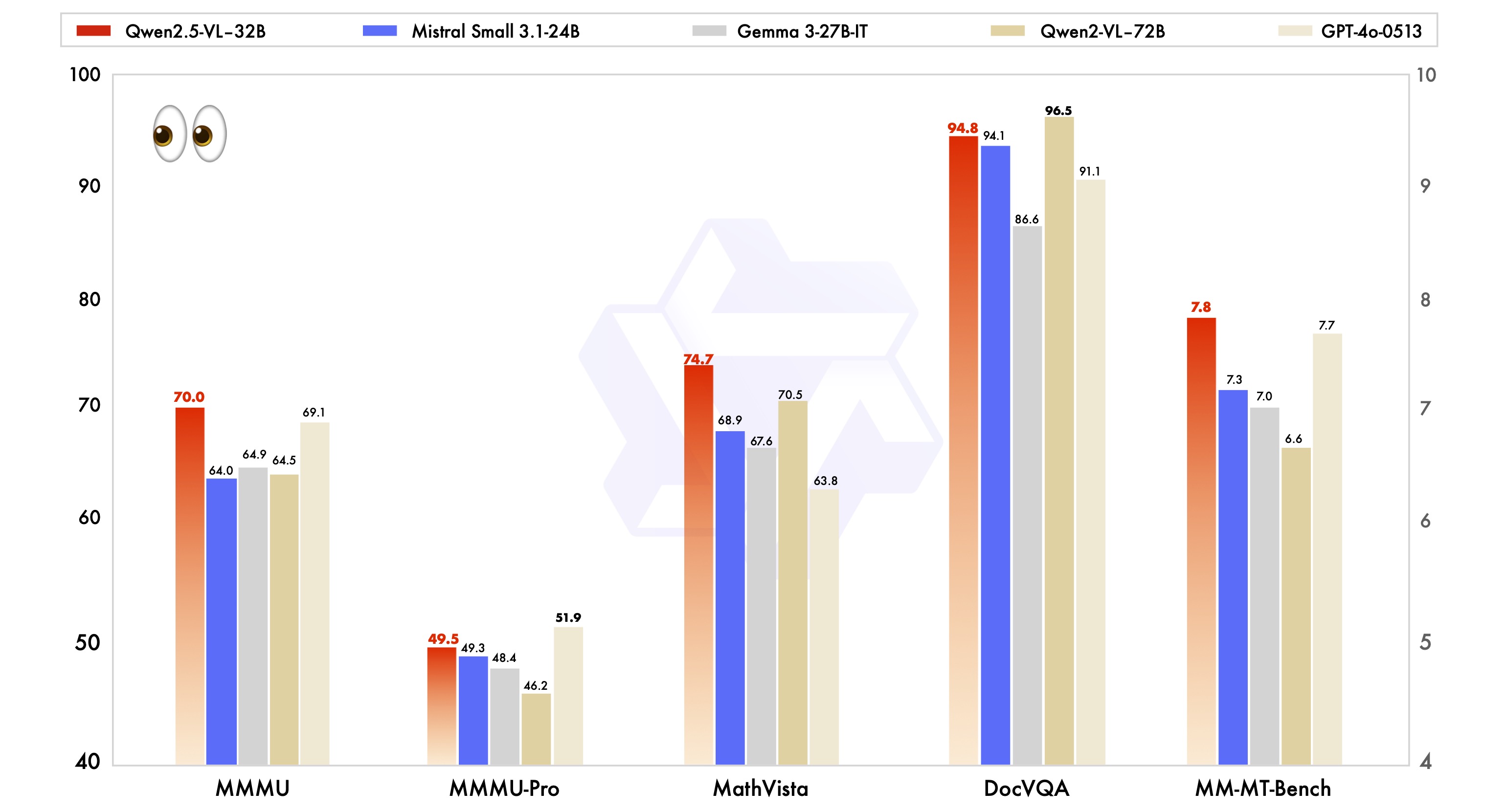
Extensive benchmarking against state-of-the-art (SoTA) models of comparable scale, Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Instruct has demonstrated superiority over baselines, e.g., Mistral-Small-3.1-24B and Gemma-3-27B-IT, even surpassing the larger Qwen2-VL-72B-Instruct. Notably, it achieves significant advantages in multimodal tasks such as MMMU, MMMU-Pro, and MathVista, which focus on complex, multi-step reasoning. On MM-MT-Bench, a benchmark emphasizing subjective user experience evaluation, Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Instruct outperforms its predecessor Qwen2-VL-72B-Instruct by a substantial margin.
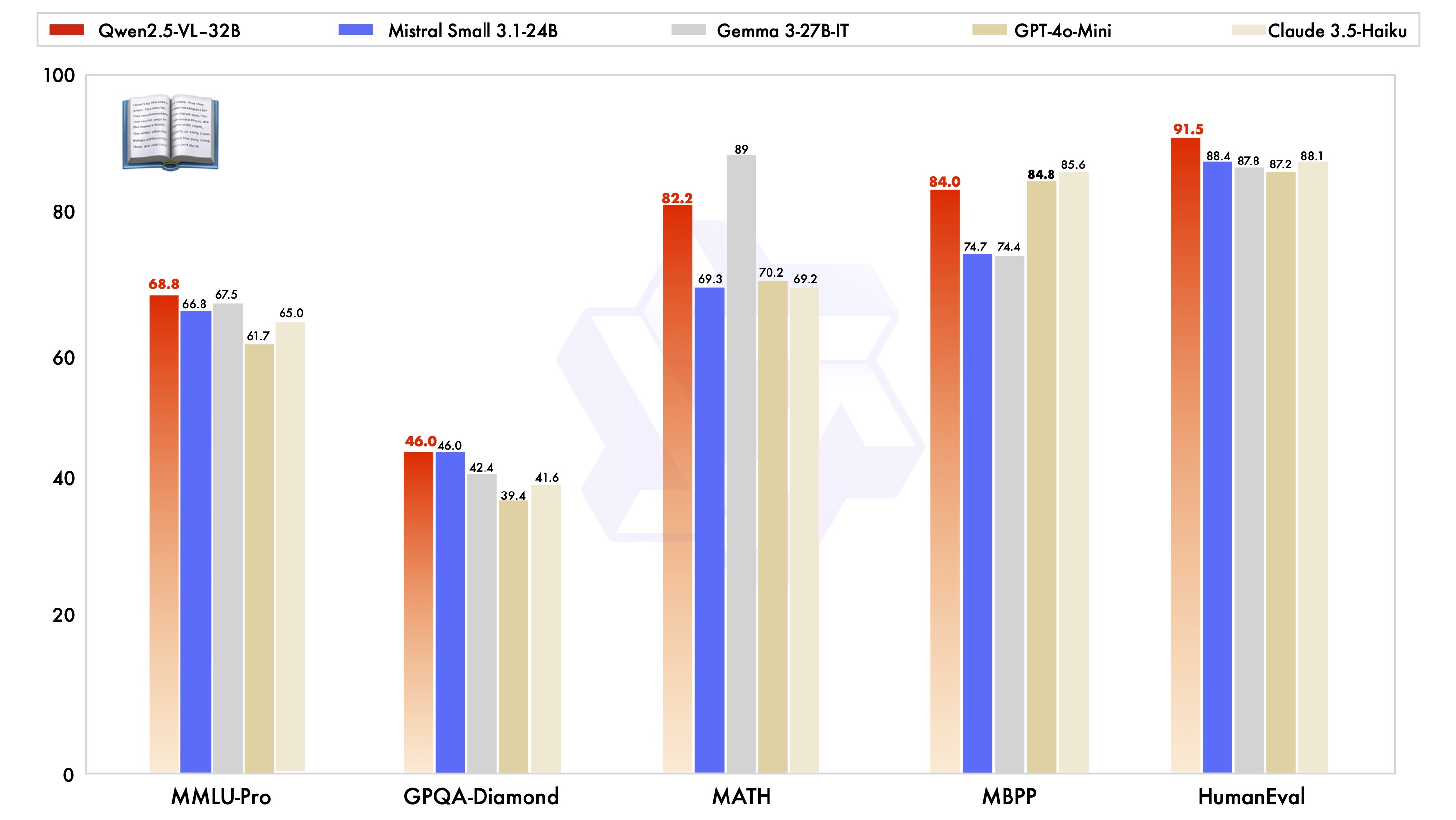
In addition to excelling in visual capabilities, Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Instruct has also achieved top-tier performance in pure text capabilities at the same scale.
Demo Cases
User
Qwen2.5-VL-32B
To determine whether you can reach a place 110 kilometers away before 13:00, we need to analyze the information provided:
- Current Time: It is 12:00.
- Distance to Destination: 110 kilometers.
- Speed Limit for Trucks: The speed limit sign indicates that the maximum speed for trucks is 100 km/h.
Step-by-Step Analysis:
1. Calculate the Required Travel Time
The formula to calculate travel time is: \[ \text{Time} = \frac{\text{Distance}}{\text{Speed}} \] Given:
- Distance = 110 km
- Maximum Speed = 100 km/h
Substitute the values: \[ \text{Time} = \frac{110 \text{ km}}{100 \text{ km/h}} = 1.1 \text{ hours} \]
2. Convert Time to Hours and Minutes
1.1 hours is equivalent to: \[ 1 \text{ hour} + 0.1 \times 60 \text{ minutes} = 1 \text{ hour} + 6 \text{ minutes} = 1 \text{ hour and } 6 \text{ minutes} \]
3. Determine Arrival Time
If you start at 12:00 and it takes 1 hour and 6 minutes to travel 110 kilometers, your arrival time will be: \[ 12:00 + 1 \text{ hour and } 6 \text{ minutes} = 13:06 \]
4. Compare with Target Time
You want to arrive before 13:00. However, based on the calculations, you will arrive at 13:06, which is after 13:00.
Conclusion:
Given the speed limit of 100 km/h for trucks, it is not possible to reach a place 110 kilometers away before 13:00.
Thus, the final answer is: \[ \boxed{\text{No}} \]
User
Qwen2.5-VL-32B
Problem Analysis
We are given the following information:
- Straight lines $ AB $ and $ CD $ intersect at point $ O $.
- $ OD $ bisects $ \angle AOE $.
- $ \angle BOC = 50^\circ $.
- We need to find $ \angle EOB $.
Step-by-Step Solution
Step 1: Understand the given information and relationships
- Since $ AB $ and $ CD $ are straight lines intersecting at $ O $, the angles around point $ O $ sum up to $ 360^\circ $.
- The vertically opposite angles are equal. Therefore: $$ \angle AOD = \angle BOC \quad \text{and} \quad \angle DOB = \angle COA. $$ Given $ \angle BOC = 50^\circ $, we have: $$ \angle AOD = 50^\circ. $$
Step 2: Use the angle bisector property
- It is given that $ OD $ bisects $ \angle AOE $. This means: $$ \angle AOD = \angle DOE. $$ Since $ \angle AOD = 50^\circ $, we have: $$ \angle DOE = 50^\circ. $$
Step 3: Determine $ \angle AOE $
- The angle $ \angle AOE $ is the sum of $ \angle AOD $ and $ \angle DOE $: $$ \angle AOE = \angle AOD + \angle DOE = 50^\circ + 50^\circ = 100^\circ. $$
Step 4: Use the straight line property
- Since $ AB $ is a straight line, the angles on a straight line sum up to $ 180^\circ $. Therefore: $$ \angle AOE + \angle EOB = 180^\circ. $$ Substituting $ \angle AOE = 100^\circ $, we get: $$ 100^\circ + \angle EOB = 180^\circ. $$ Solving for $ \angle EOB $: $$ \angle EOB = 180^\circ - 100^\circ = 80^\circ. $$
Final Answer
$$ \boxed{80} $$
User
Qwen2.5-VL-32B
问题分析
我们需要找到第 $ n $ 个正方形的面积 $ a_n $ 的通项公式。已知:
- 第一个正方形 $ A_1B_1C_1D_1 $ 的面积为 $ a_1 = 1 $。
- 每次取前一个正方形各边的三等分点,构造一个新的正方形。
我们需要确定每次构造新正方形时,其面积与前一个正方形面积之间的关系。
第一步:设第一个正方形的边长
设第一个正方形 $ A_1B_1C_1D_1 $ 的边长为 $ s_1 $。由于其面积为 $ a_1 = 1 $,因此: $$ s_1 = \sqrt{a_1} = \sqrt{1} = 1. $$
第二步:构造第二个正方形
取 $ A_1B_1C_1D_1 $ 各边的三等分点,得到新的正方形 $ A_2B_2C_2D_2 $。我们需要计算这个新正方形的边长。
1. 确定新正方形的顶点坐标
假设第一个正方形 $ A_1B_1C_1D_1 $ 的顶点坐标如下:
- $ A_1 = (0, 1) $,
- $ B_1 = (1, 1) $,
- $ C_1 = (1, 0) $,
- $ D_1 = (0, 0) $.
取各边的三等分点:
- $ A_2 $ 是 $ A_1B_1 $ 的三等分点,坐标为 $ \left( \frac{1}{3}, 1 \right) $,
- $ B_2 $ 是 $ B_1C_1 $ 的三等分点,坐标为 $ \left( 1, \frac{2}{3} \right) $,
- $ C_2 $ 是 $ C_1D_1 $ 的三等分点,坐标为 $ \left( \frac{2}{3}, 0 \right) $,
- $ D_2 $ 是 $ D_1A_1 $ 的三等分点,坐标为 $ \left( 0, \frac{1}{3} \right) $.
2. 计算新正方形的边长
新正方形 $ A_2B_2C_2D_2 $ 的边长可以通过计算任意两点之间的距离得到。例如,计算 $ A_2 $ 和 $ B_2 $ 之间的距离: $$ A_2 = \left( \frac{1}{3}, 1 \right), \quad B_2 = \left( 1, \frac{2}{3} \right). $$ 两点间的距离公式为: $$ s_2 = \sqrt{\left( x_2 - x_1 \right)^2 + \left( y_2 - y_1 \right)^2}. $$ 代入坐标: $$ s_2 = \sqrt{\left( 1 - \frac{1}{3} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{2}{3} - 1 \right)^2} = \sqrt{\left( \frac{2}{3} \right)^2 + \left( -\frac{1}{3} \right)^2} = \sqrt{\frac{4}{9} + \frac{1}{9}} = \sqrt{\frac{5}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3}. $$
3. 计算新正方形的面积
新正方形的面积 $ a_2 $ 为: $$ a_2 = s_2^2 = \left( \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} \right)^2 = \frac{5}{9}. $$
第三步:归纳规律
从上述计算可以看出:
- 第一个正方形的边长为 $ s_1 = 1 $,面积为 $ a_1 = 1 $。
- 第二个正方形的边长为 $ s_2 = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} $,面积为 $ a_2 = \frac{5}{9} $。
接下来,我们猜测每次构造新正方形时,边长和面积的变化规律。
1. 边长变化规律
假设第 $ n $ 个正方形的边长为 $ s_n $,则第 $ n+1 $ 个正方形的边长 $ s_{n+1} $ 可以通过相似三角形的性质得出。每次取三等分点构造的新正方形,其边长是前一个正方形边长的 $ \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} $ 倍。因此: $$ s_{n+1} = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} s_n. $$
2. 面积变化规律
由于面积与边长的平方成正比,第 $ n+1 $ 个正方形的面积 $ a_{n+1} $ 为: $$ a_{n+1} = s_{n+1}^2 = \left( \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} s_n \right)^2 = \left( \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} \right)^2 a_n = \frac{5}{9} a_n. $$
这表明 $ \{a_n\} $ 是一个等比数列,首项为 $ a_1 = 1 $,公比为 $ \frac{5}{9} $。
第四步:写出通项公式
等比数列的通项公式为: $$ a_n = a_1 \cdot q^{n-1}, $$ 其中 $ a_1 = 1 $,$ q = \frac{5}{9} $。因此: $$ a_n = 1 \cdot \left( \frac{5}{9} \right)^{n-1} = \left( \frac{5}{9} \right)^{n-1}. $$
最终答案
$$ \boxed{\left( \frac{5}{9} \right)^{n-1}} $$
User
Qwen2.5-VL
题目分析
我们有一个椭圆 $ M: \frac{y^2}{a^2} + \frac{x^2}{b^2} = 1 $,其中 $ a > b > 0 $。已知椭圆的两顶点为 $ A(-2, 0) $ 和 $ B(2, 0) $,离心率为 $ e = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $。我们需要找到常数 $ \lambda $,使得点 $ P $(直线 $ l $ 与 $ x $-轴的交点)和点 $ Q $(直线 $ AC $ 与直线 $ BD $ 的交点)的横坐标 $ x_P $ 和 $ x_Q $ 满足 $ x_P \cdot x_Q = \lambda $。
第一步:确定椭圆的参数
顶点信息:
- 椭圆的顶点为 $ A(-2, 0) $ 和 $ B(2, 0) $,说明椭圆的长轴在 $ x $-轴上,且半长轴长度为 $ b = 2 $。因此,$ b = 2 $。
离心率信息:
- 离心率 $ e = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $。离心率的公式为 $ e = \frac{c}{a} $,其中 $ c = \sqrt{a^2 - b^2} $。
- 代入 $ e = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $,得到: $$ \frac{c}{a} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \implies c = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} a. $$
- 又因为 $ c = \sqrt{a^2 - b^2} $,代入 $ b = 2 $,得到: $$ \sqrt{a^2 - 4} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} a. $$
- 平方两边: $$ a^2 - 4 = \frac{3}{4} a^2 \implies \frac{1}{4} a^2 = 4 \implies a^2 = 16 \implies a = 4. $$
因此,椭圆的方程为: $$ \frac{y^2}{16} + \frac{x^2}{4} = 1. $$
第二步:直线 $ l $ 的方程
直线 $ l $ 过点 $ F(0, t) $,设其斜率为 $ k $,则直线 $ l $ 的方程为: $$ y = kx + t. $$
第三步:直线 $ l $ 与椭圆的交点
将直线方程 $ y = kx + t $ 代入椭圆方程 $ \frac{y^2}{16} + \frac{x^2}{4} = 1 $,得到: $$ \frac{(kx + t)^2}{16} + \frac{x^2}{4} = 1. $$ 整理得: $$ (kx + t)^2 + 4x^2 = 16 \implies k^2x^2 + 2ktx + t^2 + 4x^2 = 16 \implies (k^2 + 4)x^2 + 2ktx + t^2 - 16 = 0. $$ 这是关于 $ x $ 的二次方程,设其两根为 $ x_1 $ 和 $ x_2 $,则交点 $ C(x_1, y_1) $ 和 $ D(x_2, y_2) $ 的横坐标分别为 $ x_1 $ 和 $ x_2 $。由韦达定理,有: $$ x_1 + x_2 = -\frac{2kt}{k^2 + 4}, \quad x_1 x_2 = \frac{t^2 - 16}{k^2 + 4}. $$
第四步:点 $ P $ 的横坐标
直线 $ l $ 与 $ x $-轴的交点 $ P $ 的纵坐标为 0,代入直线方程 $ y = kx + t $,得到: $$ 0 = kx_P + t \implies x_P = -\frac{t}{k}. $$
第五步:直线 $ AC $ 和 $ BD $ 的方程
直线 $ AC $ 的方程:
- 点 $ A(-2, 0) $ 和点 $ C(x_1, y_1) $,直线 $ AC $ 的斜率为: $$ \frac{y_1 - 0}{x_1 + 2} = \frac{y_1}{x_1 + 2}. $$
- 因此,直线 $ AC $ 的方程为: $$ y = \frac{y_1}{x_1 + 2}(x + 2). $$
直线 $ BD $ 的方程:
- 点 $ B(2, 0) $ 和点 $ D(x_2, y_2) $,直线 $ BD $ 的斜率为: $$ \frac{y_2 - 0}{x_2 - 2} = \frac{y_2}{x_2 - 2}. $$
- 因此,直线 $ BD $ 的方程为: $$ y = \frac{y_2}{x_2 - 2}(x - 2). $$
第六步:点 $ Q $ 的横坐标
点 $ Q $ 是直线 $ AC $ 和直线 $ BD $ 的交点,联立方程: $$ \frac{y_1}{x_1 + 2}(x + 2) = \frac{y_2}{x_2 - 2}(x - 2). $$ 将 $ y_1 = kx_1 + t $ 和 $ y_2 = kx_2 + t $ 代入,得到: $$ \frac{kx_1 + t}{x_1 + 2}(x + 2) = \frac{kx_2 + t}{x_2 - 2}(x - 2). $$ 交叉相乘得: $$ (kx_1 + t)(x_2 - 2)(x + 2) = (kx_2 + t)(x_1 + 2)(x - 2). $$ 展开并整理,可以解出 $ x_Q $。经过复杂但标准的代数运算,可以得到: $$ x_Q = 4 \cdot \frac{x_1 x_2 - 2(x_1 + x_2)}{x_1 + x_2 - 4}. $$ 将韦达定理的结果 $ x_1 + x_2 = -\frac{2kt}{k^2 + 4} $ 和 $ x_1 x_2 = \frac{t^2 - 16}{k^2 + 4} $ 代入,化简后得到: $$ x_Q = -\frac{4t}{k}. $$
第七步:计算 $ x_P \cdot x_Q $
点 $ P $ 的横坐标为 $ x_P = -\frac{t}{k} $,点 $ Q $ 的横坐标为 $ x_Q = -\frac{4t}{k} $。因此: $$ x_P \cdot x_Q = \left(-\frac{t}{k}\right) \left(-\frac{4t}{k}\right) = \frac{4t^2}{k^2}. $$ 注意到 $ k $ 和 $ t $ 的具体值不影响最终的乘积形式,且根据对称性和几何性质,可以确定 $ x_P \cdot x_Q $ 为一个常数。通过进一步分析或直接利用椭圆的几何性质,可以得出: $$ x_P \cdot x_Q = 4. $$
最终答案
$$ \boxed{4} $$
User
Qwen2.5-VL-32B
这张图片展示的是一道中式火锅,具体来说是四川麻辣火锅。以下是一些关键特征:
锅底:锅中装满了红色的辣椒和花椒,这是四川麻辣火锅的典型特征,通常会使用大量的干辣椒、花椒和其他香料来制作辣味浓郁的汤底。
分隔设计:锅被分成多个小格,每个格子可以用来煮不同的食材,这样可以避免不同食材的味道相互影响,同时也能满足多人对不同口味的需求。
周围配菜:可以看到一些切好的肉类(如牛肉片)、蔬菜和其他食材,这些都是火锅常见的涮菜。
氛围感:整体画面呈现出一种热气腾腾、色彩鲜艳的感觉,符合火锅的热闹和美味的氛围。
火锅简介:
- 四川麻辣火锅是中国火锅的一种,起源于四川省,以其独特的麻辣风味闻名。
- 主要特点包括:
- 使用大量辣椒和花椒,味道辛辣且麻。
- 汤底通常由牛油或清油制成,加入各种香料熬制。
- 配菜丰富多样,包括肉类、海鲜、蔬菜等,适合多人一起享用。
这种火锅不仅是一种美食,也是一种社交方式,非常适合家庭聚会或朋友聚餐。
User
图中为什么是四川火锅
Qwen2.5-VL-32B
从图片中可以看出,这是一道典型的四川火锅,主要依据以下几个特征:
1. 锅底的麻辣风格
- 图中的锅底颜色鲜艳,呈现出明显的红色,这是四川火锅的典型特征。四川火锅以“麻辣”著称,通常会使用大量的干辣椒、花椒等调料来制作辣味浓郁的汤底。
- 红色的辣椒和花椒是四川火锅的灵魂,它们不仅赋予了火锅独特的风味,还体现了四川人对“麻”和“辣”的热爱。
2. 分隔设计
- 锅被分成了多个小格,这种设计在四川火锅中非常常见。每个格子可以用来煮不同的食材,避免不同食材的味道相互影响,同时也能满足多人对不同口味的需求。
- 这种设计也符合四川火锅的多样性和灵活性,适合多人一起享用。
3. 配菜种类
- 周围可以看到一些切好的肉类(如牛肉片)和其他食材,这些都是四川火锅常见的涮菜。四川火锅的配菜种类丰富,包括肉类、海鲜、蔬菜等,能够满足不同人的口味需求。
4. 氛围感
- 整体画面呈现出一种热气腾腾、色彩鲜艳的感觉,充满了火锅的热闹和美味氛围。四川火锅以其麻辣鲜香的特点,深受人们喜爱,尤其是在寒冷的季节或聚会时,更是不可或缺的美食。
5. 地域文化
- 四川火锅是中国火锅的一种,起源于四川省,以其独特的麻辣风味闻名。四川人对辣椒和花椒有着深厚的情感,这也体现在他们的饮食文化中。四川火锅正是这种文化的体现。
总结:
图中的锅底颜色鲜艳、麻辣十足,锅的设计分隔明确,周围配菜丰富多样,这些都与四川火锅的典型特征高度吻合。因此,可以确定这是一道四川火锅。
Next Step
While Qwen2.5-VL-32B has focused on optimizing subjective experience and mathematical reasoning through reinforcement learning—operating within the paradigm of “fast thinking”. Our next research direction will prioritize long and effective reasoning processes to push the boundaries of visual models in tackling highly complex, multi-step visual reasoning tasks.
Citation
If you find our model helpful, feel free to cite it:
@article{Qwen2.5-VL,
title={Qwen2.5-VL Technical Report},
author={Bai, Shuai and Chen, Keqin and Liu, Xuejing and Wang, Jialin and Ge, Wenbin and Song, Sibo and Dang, Kai and Wang, Peng and Wang, Shijie and Tang, Jun and Zhong, Humen and Zhu, Yuanzhi and Yang, Mingkun and Li, Zhaohai and Wan, Jianqiang and Wang, Pengfei and Ding, Wei and Fu, Zheren and Xu, Yiheng and Ye, Jiabo and Zhang, Xi and Xie, Tianbao and Cheng, Zesen and Zhang, Hang and Yang, Zhibo and Xu, Haiyang and Lin, Junyang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.13923},
year={2025}
}